Online Potency Calculator



The potency on 'Dried Basis' or 'Anhydrous Basis' or 'Solvent Free Basis' must be used in case if standard is dried before use.
General Formula for Assay Calculation of 'on Dried Basis' or 'Anhydrous Basis' or 'Solvent Free Basis'

Formula for Assay Calculation of 'Dried Basis' from 'As Is Basis' or 'As Such Basis'

Formula Assay Calculation of 'Anhydrous Basis' from 'As Is Basis' or 'As Such Basis'

Formula Assay Calculation of 'Solvent Free Basis' from 'As Is Basis' or 'As Such Basis'
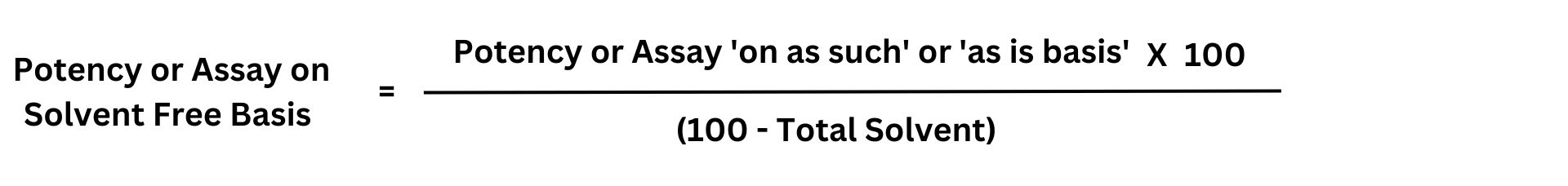
The assay content limit in almost all pharmaceutical monograms is defined on anhydrous basis. The assay test of a substance intended for medicinal application is carried out in standard analytical procedures without being rendered to anhydrous condition. Assay on an as-is basis refers to the assay test outcome. Since water is not regarded as an impurity in substances intended for medicinal use, the results of the water content test are included in the assay results in their current state. Using an industry-accepted method for assay on anhydrous basis, the water is mathematically accounted for in assay on as-is basis. The commonly used formula is written as (assay on as-is basis x 100)/(100 - % water), and the result is known as anhydrous assay.
The term "anhydrous basis" refers to a material that has not been exposed to water before analysis. It denotes the absence of any absorbed water or bound water, such as hydrates, in the sample.
The sample is weighed exactly as it was given, and any remaining moisture content is then independently determined using techniques like Karl Fischer titration or loss on drying. Water content is taken out of the sample weight while calculating the assay value.