
All about tablet tooling
1. What is the tablet tooling?
Tooling consists of three parts.
i. Upper punch
ii. Lower punch
iii. Die
2. What is meaning by one set of tablet tooling?
One set consist of one Upper punch, one Lower punch and a Die.
3. What is tooling station?
The place where one set accommodates on tablet press.
4. Explain parts of tablet tooling.
Punch terminologies:
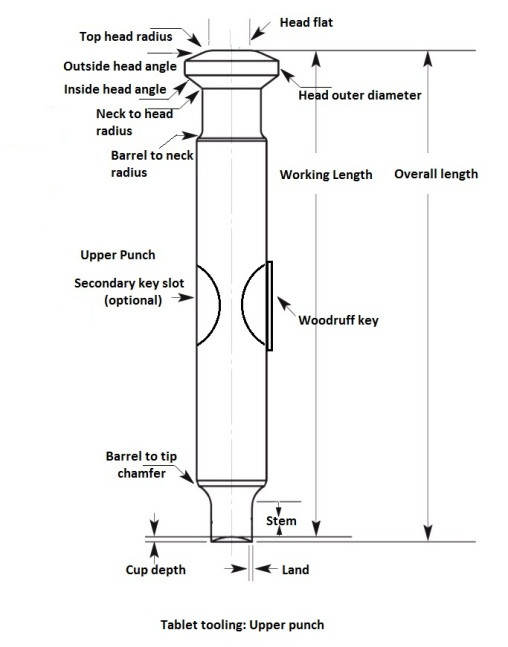
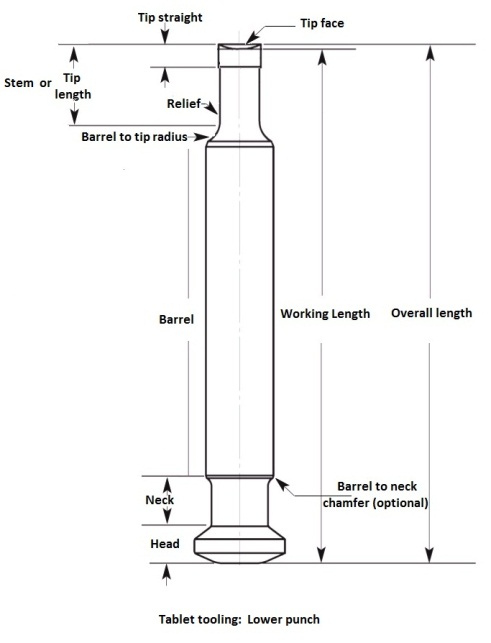
Head: Head is top part of upper and lower punch which contacts the machines cams and the pressure rollers applies the pressure to the head compress the tablets.
Head flat or Dwell Flat: Top flat area of the head. Compression force applied through the upper punch head flat and ejection pressure applied through the head flat of lower punches. Dwell time for compression is determined based on the Head flat hence, it is also called as Dwell Flat.
Outside head angle: The area touches to the pressure roller during compression operation.
Inside head angle: The part of the punch head helps upper punch to lift after compression of tablets and helps in pulls down the lower punches after ejection.
Neck: The part between head and barrel. Allow clear path to the cam.
Barrel: Allows punch to do vertical up and down movement.
Stem: Area from tip end to barrel edge.
Tip: It is the lowest portion of the punch which is responsible for shape, size and profile of the tablet.
Tip face or cup: Outer part of the tip which gives shape to the tablet. The face also will have embossing depending on the need of tablet requirement.
Tip length: The straight portion of the stem or tip.
Tip straight: The portion of tip towards the face having higher diameter of the tip.
Tip relief: Tip part other than the tip straight.
Working length: This is the distance from the head flat to bottom of the cup.
Overall length: Length from punch head flat to the tip.
Key or woodruff key: An elevated portion in the middle of the punch barrel. The key with upper punches for shaped tablets to prevent punch rotation when the punch is out of the die.
Types of heads: Domed head and Flat head
Difference between Flat head and Domed head: Domed head punches has smaller flat head. Flat head has extended head flat.
The extended head flat offers multiple benefits, including a longer dwell time (the time the head flat spends in contact with the pressure roll) at a given press speed to better compact poorly compressible products. The longer dwell time may even reduce the amount of force required to attain specific tablet hardness.
Whereas, round extended head flats don’t require keyed tooling as oval ones do, and that allows them to be used on multiple makes and models of tablet presses.
Dwell time: It is the time the head flat spends in contact with the pressure roller.
Land: The area between the outer part of the punch cup and the outside edge of the punch tip.
Cup depth: Distance between tip edge to the center point of the cup.
Barrel chamfer: Chamfers at the ends of the punch barrel.
Die terminologies:
Clearance: pace between die bore diameter and punch tip diameter
Die Bore: It is the cavity of die where granules are converted into tablet.
Die height or overall length: The height from top to bottom face of the die.
Die chamfer: This is the angle of the die bore at entry point. It guides upper punch into the die bore.
Die groove and die lock: The radial groove around the die outer diameter require locking the die into the turret with the help of die lock.
Die taper: Taper is a feature that increases the bore size at the top of the die then nominal bore size. It helps to release air from the die cavity during the compression. The feature helps to reducing tablet defects, such as capping and lamination.
Annealing: This is a heat treatment process to reduce the hardness to make it more workable. The processing done fragile punch tips to decrease the hardness of the punch cups which helps in reducing punch tip fracturing.
5. Describe about tablet tooling standards?
There are two types of standards for tablet tooling:
i. US specification provided by Tableting Specification Manual (TSM) (This is the only tooling specifications are the only published standards for the tablet compression industry). The standard is established by the American Pharmacists Association (APhA).
ii. European standard known as the EU, or “Euronorm” standard. EU, or Euronorm standard tool configurations are not published or governed by an organization or association. The EU standard is the most common tooling configuration used outside the U.S.
Reference: natoli.com
6. Differences between TSM and EU Tooling Configurations
|
Tableting Specification Manual (TSM) Tooling Configurations |
EU Tooling Configurations |
| Angled top profile | Domed head profile |
| Inside head angle for “B” punches is 37° | Inside head angle for “B” punches is 30° |
| Overall head thickness is greater in both “B” and “D” | Overall head thickness is lesser in both “B” and “D” |
| Overall punch length of the TSM tool is 0.010 inches shorter than the EU | Overall punch length of the EU tool is 0.010 inches longer than the TSM |
Reference: natoli.com
7. What are the type of tablet tooling for compression machine with die and punch dimension?
There are following six types of tablet tooling and its dimensions.
| Tooling specification | Nominal punch barrel diameter (mm) | Nominal punch die diameter (mm) | Maximum tablet diameter for round tablet (mm) | Maximum tablet diameter for shaped tablet (mm) |
|
TSM or EU B |
19 |
30.16 |
16 |
16 |
|
TSM or EU D |
25.35 |
38.1 |
25 |
25 |
|
TSM or EU BB |
19 |
24 |
13 |
14 |
|
TSM or EU DB |
25.35 |
30.16 |
19 |
19 |
|
TSM or EU BBS |
19 |
21 |
12 |
13 |
|
TSM or EU A |
12.7 |
17 |
8 |
8 |
Reference: pacifictools.in
8. What is the choice for material of construction (MoC) of Die and Punch?
1. OHNS (T) Oil Hardened Non shrinking steel (Tungsten) – AISI 01 (American Iron and Steel Institute) [Hardness: 58-59]
2. HCHC – High carbon High chromium steel – AISI D2 [Hardness: 59-60]
3. HCHC – High carbon High chromium steel – AISI D3 [Hardness: 61-62]
Note: Hardness in HRC (Hardness Rockwell C) scale

